An automotive lift is a mechanical device that elevates vehicles for maintenance, inspection, and repair. It allows technicians to perform essential tasks safely and efficiently.
The demand for space-saving, reliable, and heavy-duty lifting solutions has significantly increased in commercial workshops and high-end residential garages.
This article provides an in-depth understanding of automotive lifts, detailing their types, uses, mechanisms, capacities, and practical applications for automotive professionals and service managers.
What Is an Automotive Lift?
Automotive lifts are devices that use hydraulic, pneumatic, or mechanical force to raise and support vehicles above ground level. Lifts can be powered by electric motors, pressurized fluid, or gear-driven systems, depending on the model.
A hydraulic lift is a mechanism that utilizes a pump to inject fluid into a cylinder, thereby causing a piston to move upward and lift the vehicle. These systems are famous for their high lifting capacities, smooth operation, and adaptability to various vehicle sizes.
Lifts are crucial for accessing below-chassis components, such as brake replacements, transmission servicing, undercarriage cleaning, and exhaust work, as they require vertical clearance.
These tools provide easy access, minimize physical strain on technicians, and enhance the safety and ergonomics of the working environment, particularly for heavy vehicles or high-clearance designs like SUVs and commercial trucks.
Types of Automotive Lifts
Automotive lifts are customized to suit workshop layouts, vehicle types, and lifting requirements. The following are the most common types found in modern garages.
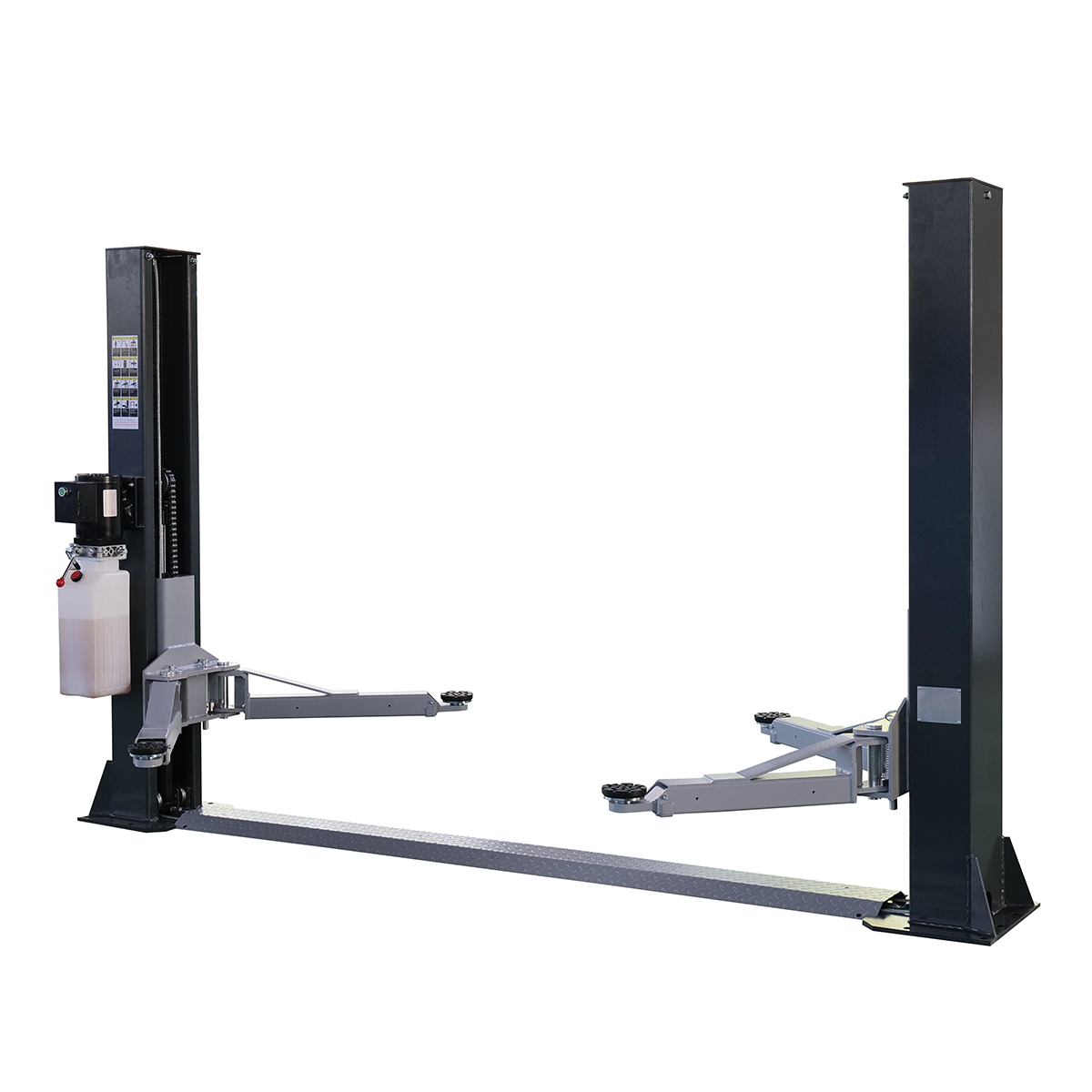

a. Two-Post Lifts
Two-post lifts are designed with adjustable arms that engage the vehicle’s frame or lifting points. It consists of two upright columns. Arms can be symmetrical, aligned with the column, or asymmetrical, angled for easier door access.
- Use Case: It is ideal for daily repair shops that handle a diverse range of vehicles.
- Pros: It is space-efficient, affordable, and versatile. Additionally, it provides easy access to the undercarriage and wheels.
- Cons: It demands precise positioning and needs a higher ceiling than some other lifts.
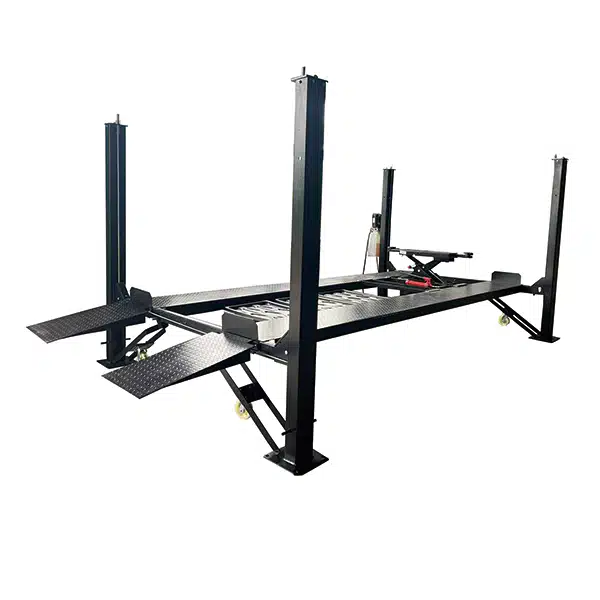
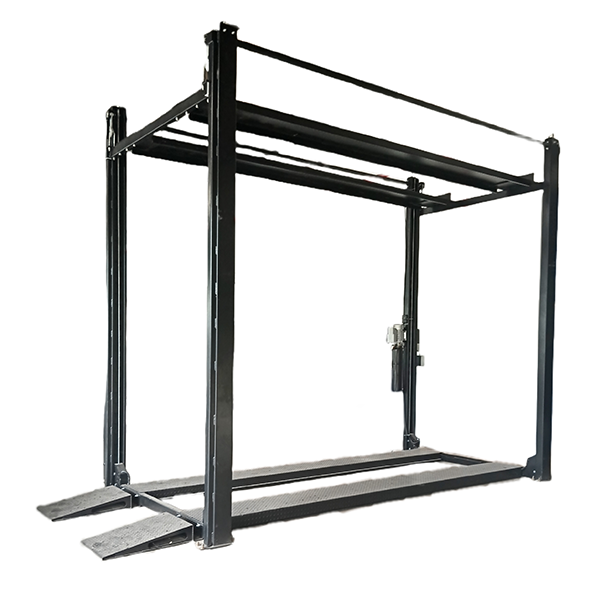
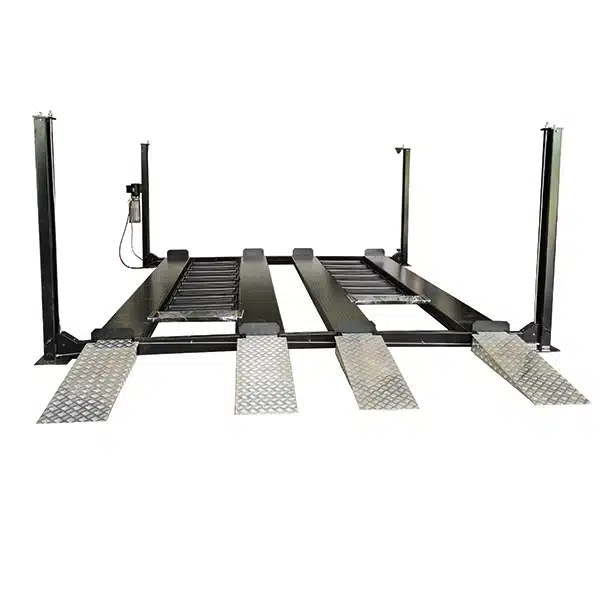
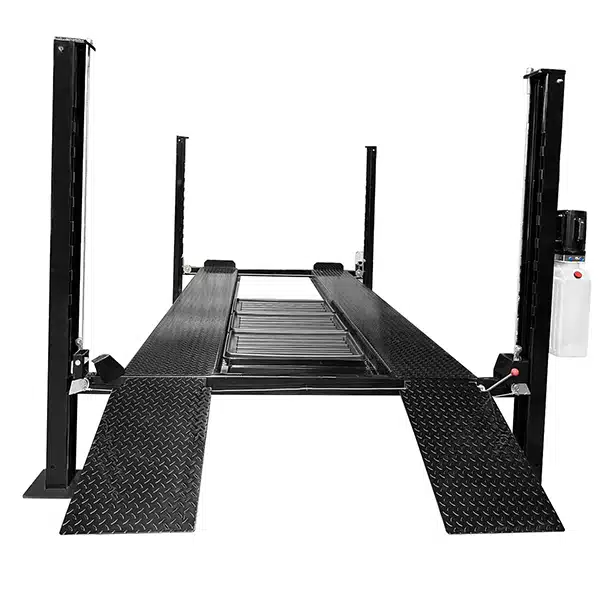
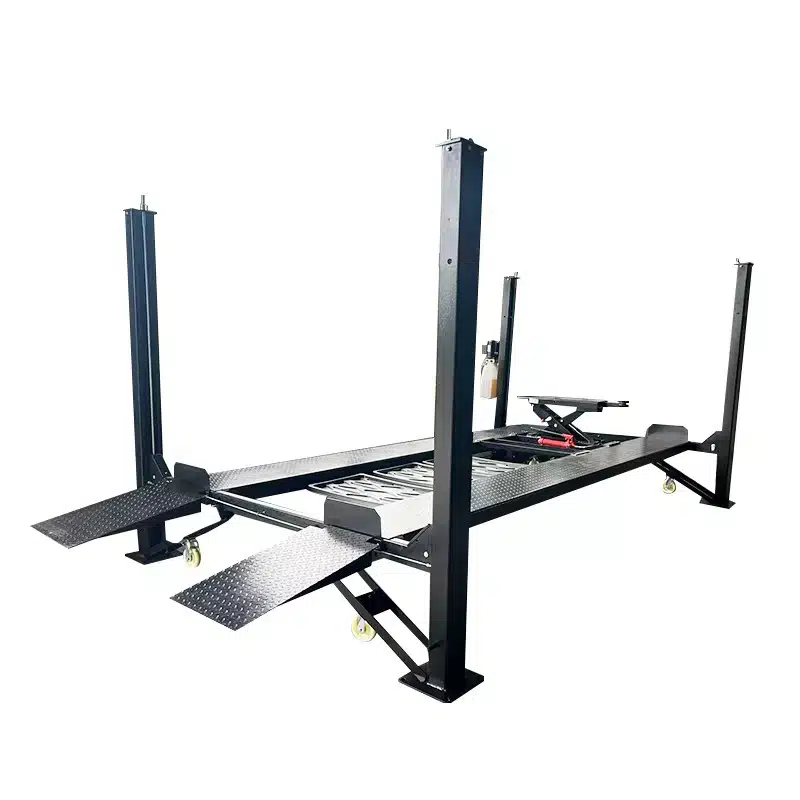
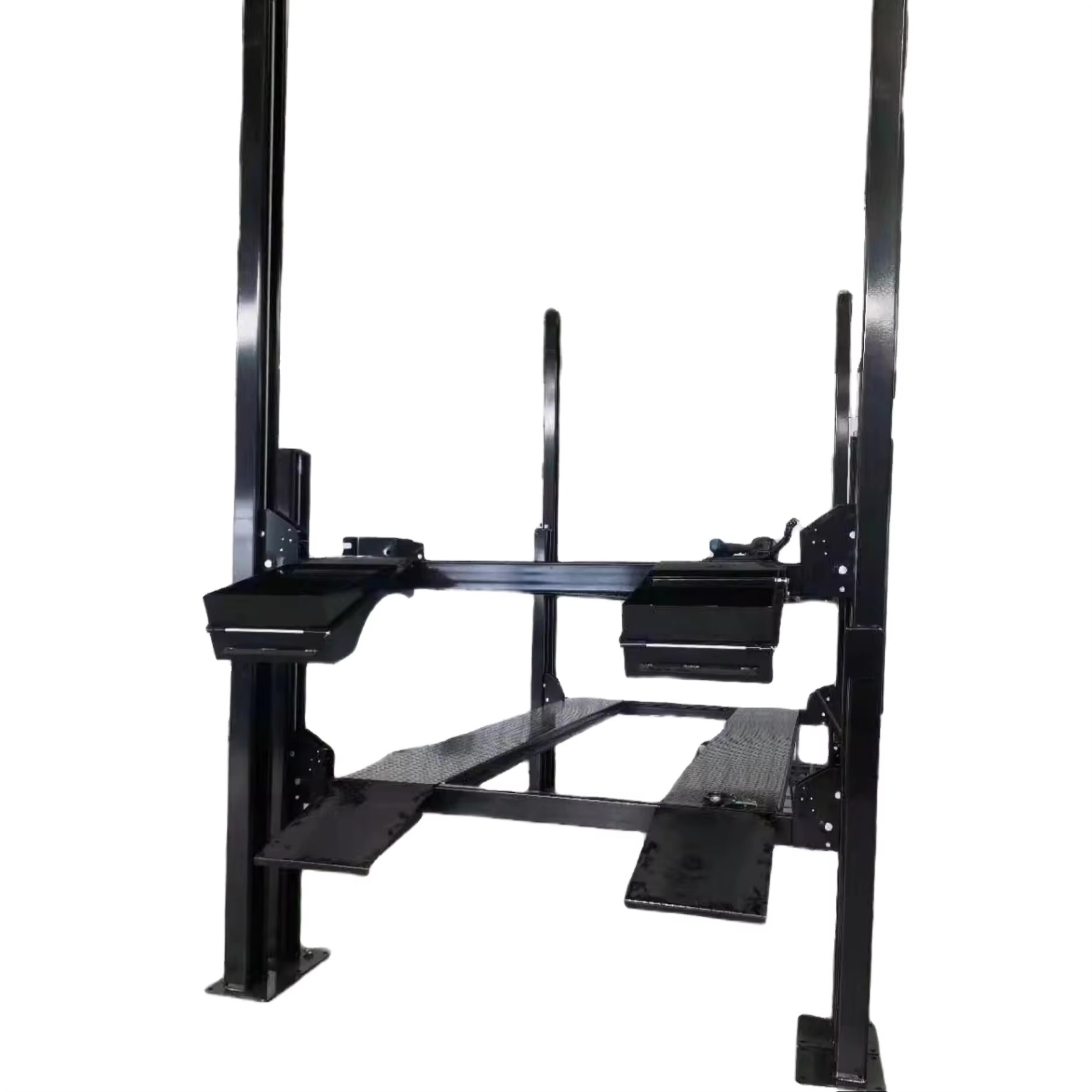
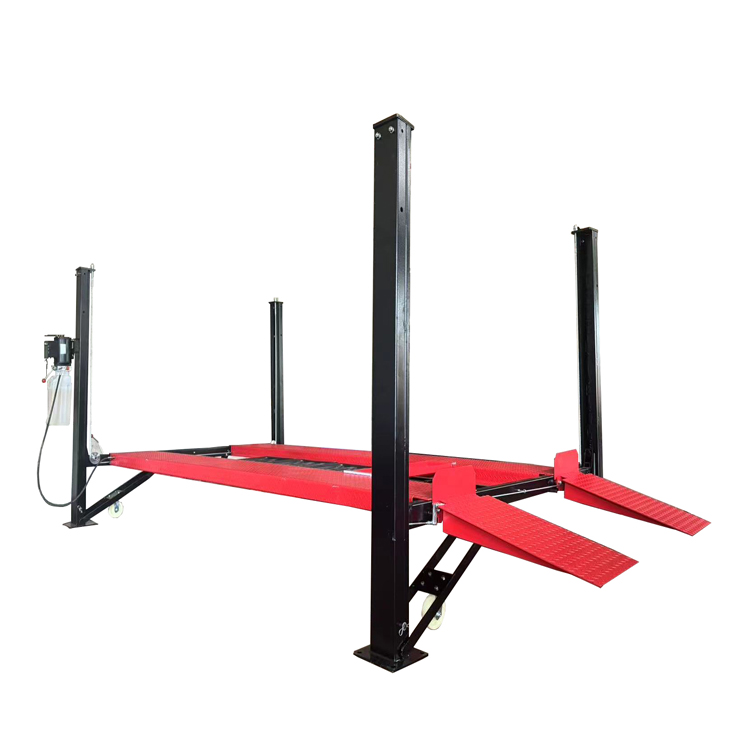
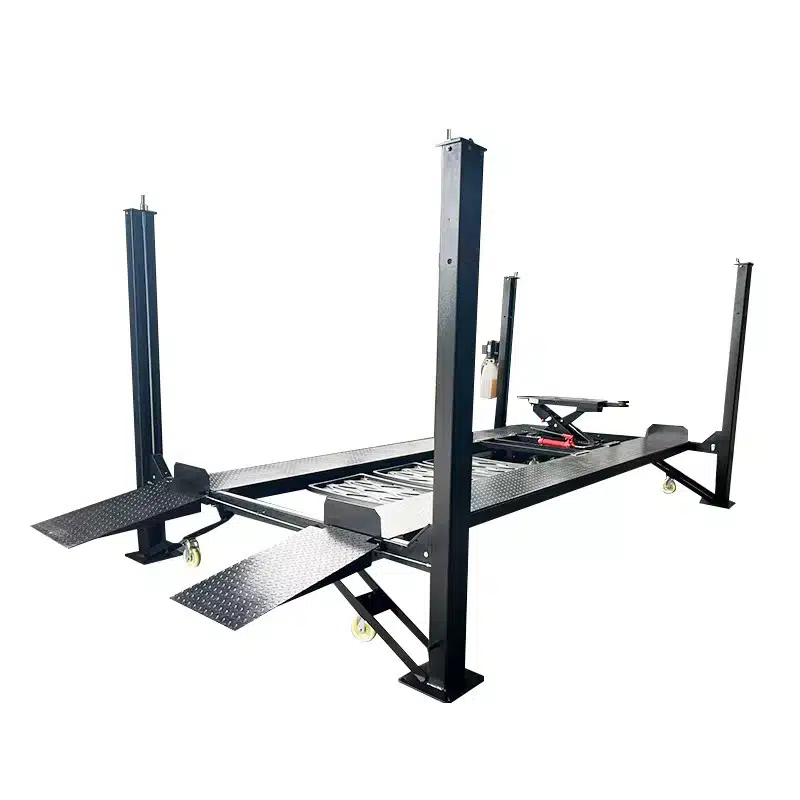
b. Four-Post Lifts
Four-post lifts are designed with drive-on ramps and four supportive columns. These models differ from two-post models as they do not lift via the chassis but instead use the vehicle’s wheels for raising.
- Use Case: This item is utilized for long-term storage, alignments, and servicing heavier vehicles like trucks or RVs.
- Pros: The vehicle offers enhanced stability and lifting capacities. It is capable of lifting up to 18,000 lbs or more. Furthermore, it eliminates the need for precise vehicle positioning.
- Cons: This method requires more floor space and is typically more expensive.
c. Scissor Lifts
Scissor lifts are vertical vehicle raising devices with X-shaped folding arms. They can be either surface-mounted or recessed into the ground.
- Use Case: It is ideal for wheel and brake services, particularly in compact urban garages.
- Pros: The compact and cost-effective design is perfect for workshops with limited space.
- Cons: The vehicle has limited undercarriage access. Therefore, it is unsuitable for all repair tasks.

d. In-Ground/Ground Lifts
In-ground lifts are concealed beneath the shop floor. The system enables the extension of lift arms or pads from concealed areas.
- Use case: This item is typically found in high-end or modern workshops that prioritize aesthetics and workspace efficiency.
- Pros: It provides easy ground access, a minimal visual footprint, and minimizes floor clutter.
- Cons: The installation process is more expensive due to the need for extensive civil work and complex maintenance.
e. Mobile Column Lifts
Mobile column lifts are wheel-mounted units that can be moved and synchronized to lift vehicles at each wheel point.
- Use Case: This product is designed for fleet maintenance, public vehicles, and heavy-duty applications weighing up to 100,000 lbs or more.
- Pros: This product offers scalability, portability, and adjustable lifting capacities. This makes it suitable for various vehicle sizes.
- Cons: Regular calibration is required, which can be costly for small garages.
Selecting the Right Lift for Your Workshop
The selection of a suitable lift necessitates a thorough assessment of various technical and operational aspects.
- Vehicle Type: Sedans and light-duty vehicles require two-post lifts, while heavy-duty vehicles require four-post or column lifts.
- Ceiling Height: Taller lifts require higher ceilings, while ground lifts and scissor models are suitable for low-clearance environments.
- Power Requirements: Lifts may require single-phase or three-phase electrical connections, which could impact their installation feasibility.
- Budget Constraints: The investment should be proportional to the size of the shop, the workload, and the anticipated return.
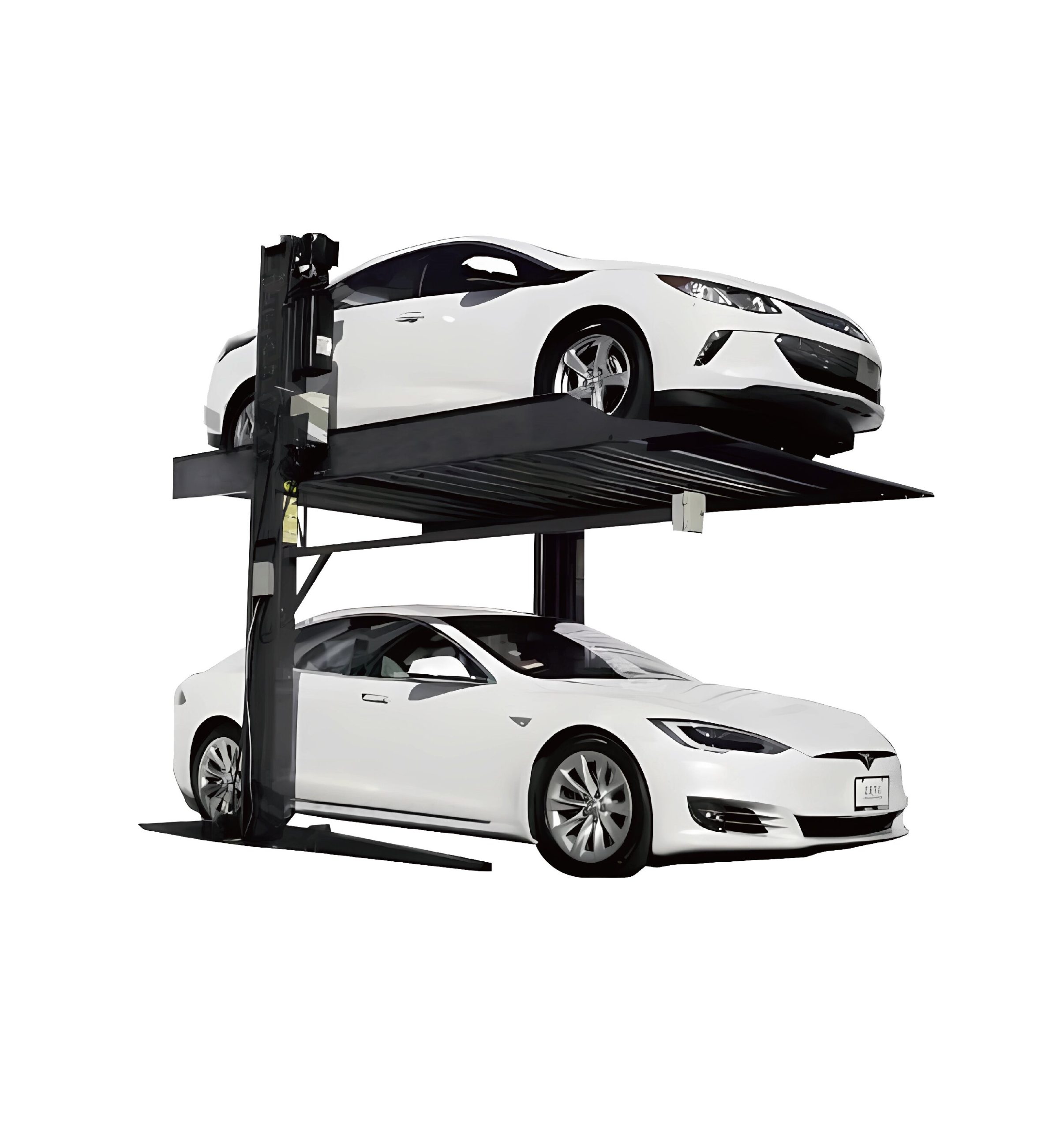

Applications in Modern Workshops
- Vehicle Inspection – Easy access to the undercarriage for thorough checks.
- Routine Maintenance – Oil changes, brake servicing, fluid refills.
- Tire and Wheel Service – Changing tires, wheel alignment, balancing.
- Suspension and Steering Repairs – Accessing components for repair or replacement.
- Exhaust System Work – Repair or replacement of exhaust pipes and mufflers.
- Transmission and Drivetrain Repairs – Servicing or replacing transmission parts.
- Chassis and Frame Work – Straightening or repairing frame damage.
- Engine and Component Removal – Facilitating removal or installation of heavy parts.
- Underbody Cleaning and Rust Proofing – Access for cleaning and protective coatings.
- Space Optimization – Stacking vehicles or parking one over another in busy workshops.
Maintenance of Automotive Lifts
Regular lift maintenance is crucial for maintaining safe operation, equipment longevity, and regulatory compliance.
- Inspection Tasks: Regularly check hydraulic fluid levels, look for leaks, and inspect lift pads, arms, and cables for any potential issues.
- Mechanical Safety: It ensures the functionality and responsiveness of locking mechanisms and emergency shutoffs for mechanical safety.
- Regulatory Standards: ANSI/ALI ALCTV (Automotive Lift Institute) standards ensure that lifts meet performance and safety standards.
Preventive maintenance is a crucial strategy that not only minimizes downtime but also reduces repair costs and ensures long-term operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Automotive lifts are essential for workshop infrastructure to address specific conditions, space limitations, and vehicle requirements. This guide on automotive lifts highlights the importance of selecting the right lifting solution for workshops, highlighting its direct impact on productivity, safety, and scalability.
The selection of the appropriate lift necessitates thorough technical analysis, operational expertise, and a comprehensive comprehension of lifting capacities, workspace layout, and long-term business objectives.
Automotive lift selection is not just about elevating vehicles; it’s about elevating performance in workshops aiming to future-proof operations.
Top Garagelift is a reputable manufacturer of reliable, workshop-grade car lifting solutions. We offer a wide range of car lifts to meet various workshop needs. Contact us today.